<primary sequence file>
The name of a file containing FASTA formatted sequences that are to be used as the primary set in PSP calculation.
<control sequence file>
The name of a file containing FASTA formatted sequences that are to be used as the control set in PSP calculation.
Output
A FASTA-like PSP format is written to standard output, it contains a prior for every position of every sequence in the primary set.
Options
| Option | Parameter | Description | Default Behavior |
|---|---|---|---|
| General Options | |||
| -minw | minw | The minimum width to use with selecting the "best" width for PSPs. | The minimum width is set to 4. |
| -maxw | maxw | The maximum width to use with selecting the "best" width for PSPs. | The maximum width is set to 20. |
| -triples | Use spaced triples instead of whole-word matches. Recommended for protein. | Whole-word matches are used. | |
| -fixedstart | When using the -triples option, only consider triples starting at the start of the site. | Allow triples to start anywhere in a width w site. | |
| -equiv | Letter Groups | Any sequence of letter that appears together should be matched as equal. Separate letter groups using "-", e.g. -equiv "IVL-HKR" means treat all occurrences of I, V or L as the same, and all occurrences of H, K or R as the same. Note that in alphabets where '-' is an allowed symbol separate groups may be specified by repeating the -equiv option for each group. | No letter groups are used. |
| -revcomp | Both strands are considered when calculating PSPs for complementable alphabets. | Only the given strand is considered. | |
| -scalemin | min score | The lowest score value after scaling. | The lowest score is set to 0.1, unless the -scalemax option is set in which case the lowest score is max score - 1. |
| -scalemax | max score | The highest score value after scaling. | The highest score is set to 0.9, unless the -scalemin option is set in which case the highest score is min score + 1. |
| -maxrange | Choose the width with the biggest difference between minimum and maximum scores (before scaling). | Choose the width with the biggest maximum score (before scaling). | |
| -raw | Output scores instead of priors. | The program output PSPs. | |
| -reportscores | Send to standard error primary and control file names, min and max scores and min and max widths, tab-separated. | Do not report scores to standard error. | |
| -verbose | Send detailed stats to standard error, reporting frequency of each score. | No extra information is reported. | |
Examples
In each example, the sequence file is the same as the positive set used
for psp-gen. While there is no check that you have done
this because MEME runs as a separate program (other than that the
sequence names need to match, as do the number of sites), using a
primary set different to the sequence set MEME searches is unlikely
to be useful.
Generate a discriminative prior for a DNA sequence set
(pos-dna.fasta) likely to contain TF binding sites, given
another DNA sequence set unlikely to contain TF binding sites
(neg-dna.fasta):
psp-gen -pos pos-dna.fasta -neg neg-dna.fasta > dna.psp
Use these position-specific priors in MEME, searching both strands:
meme pos-dna.fasta -psp dna.psp -oc meme_out_dna
-revcomp
Generate a discriminative prior for a protein sequence set
(pos-prot.fasta) associated with a specific function, given
another protein sequence set unlikely to relate to that function
(neg-prot.fasta):
psp-gen -pos pos-prot.fasta -neg neg-prot.fasta -protein
-triples -maxrange > prot.psp
Use these position-specific priors in MEME:
meme pos-prot.fasta -psp prot.psp -oc meme_out_prot
View usage information:
psp-gen -h
Detailed description
The psp-gen program generates a position-specific
prior (PSP) in a data file, which can be used as an additional input
to MEME to bias the search to sites more likely to
contain a motif (or motifs) of interest. Without using a PSP, MEME
assigns the same prior probability to all sites. A PSP is generated
by psp-gen using two sequence sets, each
in FASTA format:
- the primary set (or X) contains the same sequences as you intend to search for a motif using MEME
- the control set (or Y) is a contrasting set of sequences that is unlikely to contain the motif or motifs of interest, but is otherwise similar to the primary set.
The basic principle of a discriminative prior is to start from the question:
What fraction of all instances of a w-wide subsequence (or w-mer) across both sequence sets occur in the primary set?
The intuition is that any w-mer that is common in the primary set but not the control set could form part of motif of interest, based on the way the two sets are chosen.
PSP calculation starts from the following equation based on the
D-prior described in the Narlikar et al. RECOMB
2007 paper
"Nucleosome
Occupancy Information Improves de novo Motif
Discovery". We count the number of instances
Xi,j(w) of the
subsequence w wide starting at position j in sequence
Xi of the primary set, and similarly
count Yi,j(w) in the control
set, then calculate for each site
As pseudocounts, we add 1 to the enumerator, and 1 +
|X|/|Y| to the denominator. The purpose of the
pseudocounts is to avoid giving a high score to infrequent
subsequences that are not (or rarely) found in the control set. Once
we have scored all sites for a given value of w, we scale
scores to a range that can be set on the command
line, with the default range [0.1,0.9].
We repeat scoring for the whole range of motif widths under
consideration, and choose a "best" width using one of two methods:
either we choose the value of w that maximizes the score
over all sequences, or the value of w that maximizes the
difference between the maximum and minimum score over all
sequences. We also allow an option of using spaced triples
instead of whole words to match
subsequences. See Variations below for more
details on triples and choosing the "best" width.
Once we have scored every available site and chosen a specific value
of w, we convert the scores to probabilities, based on the
proportionalities
where Zi = j means
that the site for a motif in sequence Xi is found at
location j (with j = 0
signifying there is no site in the given sequence),
and Di,j is the score for
sequence Xi at the site starting at
location j, numbered from 1.
We convert these proportionalities to a PSP by normalizing them to add
up to 1 over each sequence.
Running with MEME
Since MEME runs as a separate program, there is no way to check that the primary set is the same as the sequence set given to MEME. There are however checks that every name in the PSP file matches a name in the MEME sequence set, and that the number of sites in the PSP file for a particular sequence name matches the number of sites in the sequence file seen by MEME. While it does not make sense to use a completely different sequence set for PSP generation and for running MEME (with the resulting PSP file), MEME can use a PSP file that does not provide probabilities for every sequence. Any sequences not in the PSP file are given a uniform prior probability. MEME documentation includes more detail on how PSPs are used.
Variations
For each variation, "default" means that you do not need to specify a command-line switch to turn on that setting.
- sequence alphabet: choose -dna
(default), -rna or -protein.
For DNA, you also have the option to score matches on both strands:
-revcomp(the default is to score only the given strand). This setting applies to both the primary and control sequences.
- choosing the "best" width: specifying
-maxwand-minwprovides limits topsp-genbut the algorithm chooses one width to generate priors after scoring the range of allowed widths, using one of two variations: - maximum score (default): choose the value of w that maximizes the score over all sequences.
- maximum range of values (
-maxrange): choose the value of w that maximizes the difference between the highest and lowest score over all sequences. This variant is useful in data sets where a high number of sites achieve similar high scores (more likely to happen with protein sequences). - type of word match:
- whole-word match (default)
- spaced triples (
-triples): for a case where exact-word matches are unlikely to succeed, spaced triples are an alternative. Each w-wide word is broken down into triples containing an initial, middle and final letter, and all other letters are treated as don't cares (i.e., they match anything). In spaced triples mode,psp-genscores a site on the basis of the spaced triple fitting the w-wide word at that site that has the highest score. For example, the subsequence
MTFEKIcontains the following triples:
MT...I
M.F..I
M..E.I
M...KI
where "." matches anything when counting matches.- An option that only applies to triples
is
-fixedstart, which only allows triples for the current site under consideration that start at the beginning of the site. This option reduces execution time at the expense of considering fewer possibilities for scoring a site. - default: consider triples of all widths that fit the current site.
- An option that only applies to triples
is
- scaling variations (
-scaleminand-scalemax): the scoring formula creates values in the range[0,1], but the conversion to PSPs from scores requires values strictly less than 1. Choosing an option other than scaling between the default[0.1,0.9]reduces (if you narrow the range) or increases (if you widen the range) sensitivity to small differences in scores. If you only set one ofscaleminorscalemax, the other is calculated as described in Options. - ambiguous characters: you have two levels of control of
ambiguous characters:
- ambiguous characters in the sequence data: The effect of encountering any of these letters is to score a word or triple containing them as if it only occurs once, to minimize its score.
- treat specific letters as equivalent: use
the
-equivoption to treat specific groups of letters as if they were all the same (default: all letters are treated as unique). For more detail, see Options.
- reporting and debugging: you have various options for
understanding better how PSPs are calculated.
- see raw scores:
-rawstops the last stage of computation that converts the scores to probabilities; the scores sent to standard out are however scaled, using either the defaults or selected values ofscaleminandscalemax(default: convert scores to PSPs). - report range of scores:
see
-reportscoresin Options (default: do not report). - see detailed statistics:
-verbosecauses detailed statistics on scores to be sent to standard error (default: no statistics reported).
- see raw scores:
Performance scalability
The running time of psp-gen scales linearly in the sizes of the positive and negative sequence sets (X and Y), and faster than linearly in the difference between the maximum and minimum motif widths (N = maxw-minw). Running time using the default method (exact word match) is O((|X| + |Y|)(Nlog(N))). Running time using the spaced triples method (option -triples) is approximately O((|X| + |Y|)(Nlog2(N))).
The plots below show actual running times of psp-gen on a 4 GHz Intel Core i7 processor with 16GB of memory on inputs containing different numbers of sequences in the positive and negative sets, and specifying different values of the maximum motif width (option -maxw), and different methods—exact word match (default) or spaced triples (option -triples)
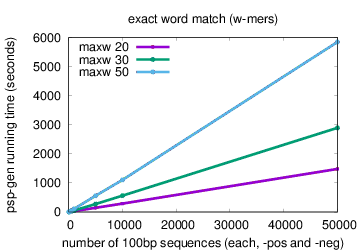 |
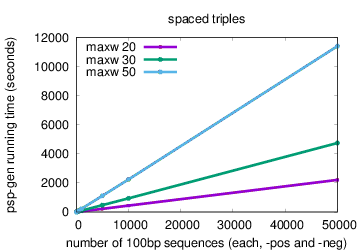 |
Known problems
- Any letters in sequence representing ambiguous bases or amino acids result in a word (w-mer) containing that word (or triple in the case of protein) being counted whether in the primary or control sets as if it occurred once, to minimize its score.